No products in the cart.
Counterfeit Money
Examples of Money Laundering and Understanding the Three Stages
what is an example of money laundering?
Examples of money laundering is an activity that has far reaching consequences worldwide. Because it involves a process of disguising illegally obtained funds to make them seem legal. So, In this blog post we will explore the concept of money laundering its definition, the three stages involved and present real-life instances that highlight the prevalence of this illegal practice.
What exactly is money laundering?
Money laundering refers to the process of disguising the source of obtained funds often acquired through criminal activities in order to make them appear legitimate. Because this illicit practice involves a series of transactions, with the ultimate aim of legitimizing unlawfully acquired profits.
Definition of Money Laundering:
Within a framework money laundering is commonly defined as engaging in transactions with the intention to conceal the origin, source or destination of unlawfully obtained money. Because The process entails manipulating the system to give an appearance of legitimacy to illicit funds allowing wrongdoers to enjoy their gotten gains without raising suspicion.
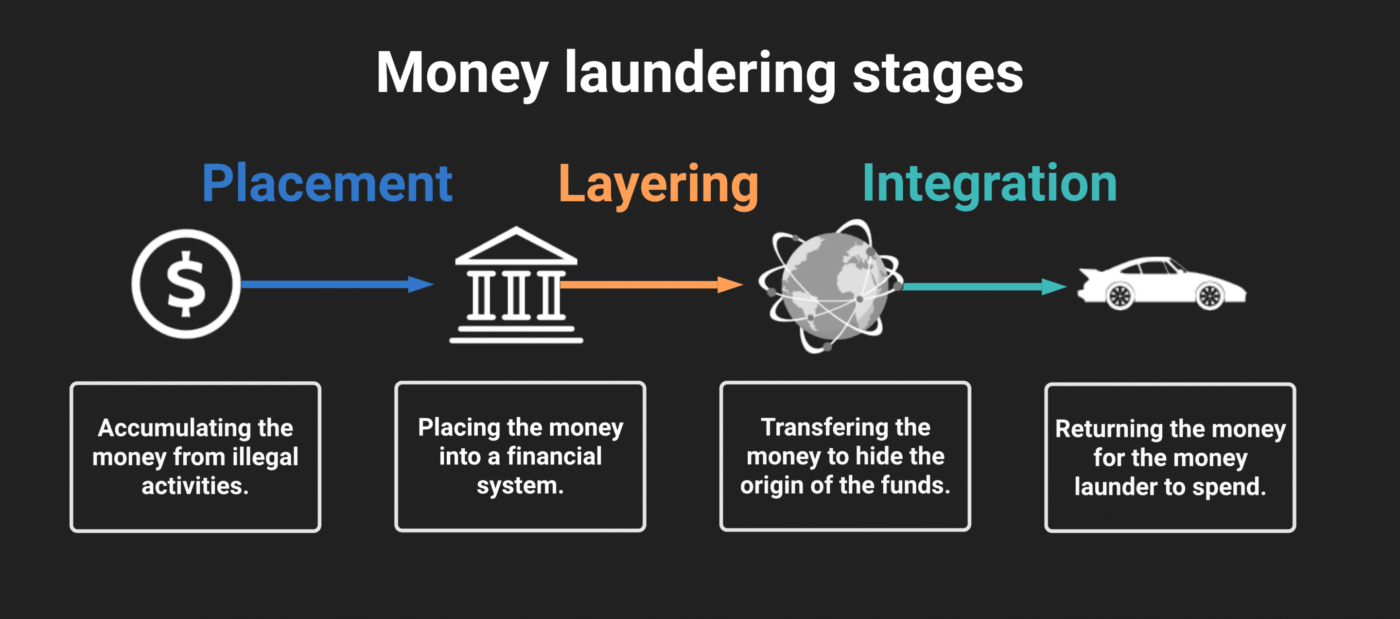
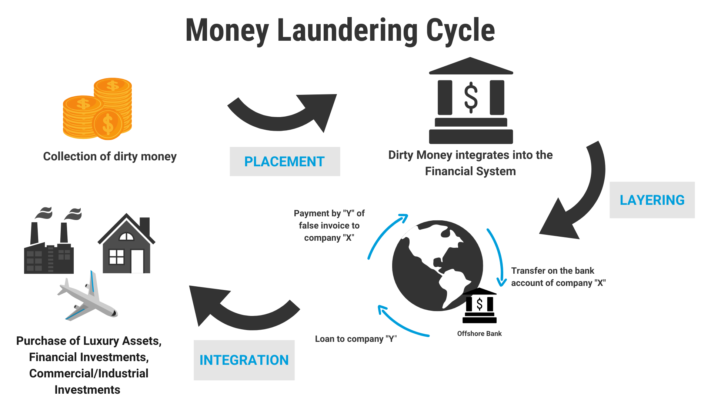
Three Stages of Money Laundering:
Money laundering typically encompasses three stages, each serving a purpose within the overall process.
Placement: In this stage illegal funds are introduced into the system. Because This can be achieved through means such as depositing amounts of cash into banks acquiring valuable assets or participating in activities, like gambling. So, The objective is to distance the money from its origins.
Distribution: Distribution phase aims to further cover sources of funds by establishing strong financial links. Because This includes transferring funds between accounts, buying and selling securities, or other transactions that make it difficult for officials to determine the source of the funds
Integration: The final step is to reintroduce the “cleaned” money back into the economy, making it appear to come from a legitimate source. This may include investing in legitimate businesses, owning property, or buying expensive goods. So The consolidation measure aims to reinforce the illusion that the money is legitimate and has nothing to do with criminal activities.
Examples of money laundering:
Shell Companies: The most common approach is to create shell companies, which are companies that exist only on paper and have no real operations. Criminals use these organizations to disguise their assets and facilitate the movement of illegal funds across borders. The 2016 Panama Papers leaks revealed several examples of shell companies being used to launder money from individuals and organizations.
Real estate: Speculators often invest in real estate to stabilize their money. Illegally obtained money can be used to buy expensive real estate, making it appear that the money is coming from a legitimate source. This can be especially difficult to research, as real estate transactions can be complex and involve many parties.
Cryptocurrency transactions: The rise of cryptocurrencies has created new challenges in the fight against money laundering. Criminal suspects can use digital currencies to transfer and store illegal funds Providing anonymity. Authorities are increasingly scrutinizing cryptocurrency exchanges and transactions to curb money laundering in the digital sphere.
Trade-based money laundering: Criminals can manipulate international trade to launder money. This may involve overpricing or underfunding of goods and services, allowing money to be moved across borders without arousing suspicion. The use of global trade complexity allows money launderers to conceal the true nature of their financial activities.
- These small amounts are then deposited in separate accounts, making it more difficult for authorities to detect and pursue suspicious transactions
Anti-money laundering efforts:
Governments and financial institutions around the world have implemented anti-money laundering (AML) measures to address the widespread issue of money laundering and these include measures a robust process for identifying your customers (KYC), monitoring transactions and reporting suspicious activities. International cooperation is also needed, as money laundering often crosses borders and requires significant efforts to track and apprehend criminals.
money laundering definition
Exactly. Money laundering is a crime in almost every jurisdiction. Laws and regulations have been developed to prevent and prosecute individuals involved in money laundering activities.
how to launder cash?
Penalties for money laundering can range from fines to life imprisonment, indicating how seriously authorities take this illegal activity. Money laundering is a major challenge for law enforcement agencies, financial institutions and government. Examples of money laundering.